The Future of Enterprise Solutions
March 28, 2024Discover how AI, cloud integration, and IoT are shaping the future of enterprise...
Read moreComputerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) have become the backbone of modern maintenance operations, empowering organizations to plan, track, and optimize every facet of their asset lifecycle. But not all CMMS platforms are created equal. Behind the sleek interfaces and marketing buzz lies a complex tapestry of modules each handling distinct functions, from work order management to financial reporting, from preventive maintenance scheduling to barcode-enabled mobile workflows.
In this blog, we’ll explore the vast landscape of CMMS technology modules, unpack the key capabilities each brings to the table, and share insights on how to interpret module ratings to choose (or fine-tune!) the right CMMS for your organization.

At its core, a CMMS is a collection of interrelated modules, each responsible for a slice of maintenance management:
General CMMS Functionality: The foundation dashboarding, basic reporting, and system administration.
Maintenance Management: Work order creation, scheduling, and execution.
Preventive & Predictive Maintenance: Automated scheduling, condition-based alerts, and calibration tracking.
Asset & Inventory Management: Parts tracking, purchasing requisitions, vendor contracts, and stock allocations.
Human Resources & Training: Skills matrices, certifications, and workforce planning.
Financials & Reporting: Cost accounting, budgeting, general ledger integration, and KPI dashboards.
Mobility & Automation: Handheld device support, barcode scanning, offline data sync, and 3rd-party shop-floor or PDM integrations.
In the image above, you can see a comprehensive list of over thirty distinct module families everything from “Vehicle Maintenance” to “Forecasting,” “Workflow” to “Employee Self-Service.” Let’s tackle them in logical groupings.
Work orders are the lifeblood of any maintenance operation. A robust module should allow you to:
Create and assign work orders with defined steps, required parts, and estimated labor.
Track status (Open, In Progress, On Hold, Completed) in real time.
Log actual hours and materials against each order for accurate costing.
Why It Matters: Detailed work orders provide the data historians and analysts need to spot recurring failures, balance technician workloads, and drive continuous improvement.
Preventive maintenance (PM) modules schedule routine tasks oil changes, inspections, filter replacements based on time, usage, or condition triggers. Advanced systems also offer:
Calibration Management: Ensuring measurement devices remain accurate.
Condition Monitoring & Alarms: Real-time telemetry (vibration, temperature) feeding automated alerting.
Why It Matters: By shifting from reactive to proactive maintenance, you reduce unplanned downtime, extend asset life, and improve safety.
Some organizations need specialized workflows for fleets, for regulatory inspections, for industry-specific compliance. A “Vehicle Maintenance” module might include license renewals, odometer-based services, or tire rotation schedules.
Why It Matters: Tailored modules reduce customization overhead and ensure your CMMS “speaks the language” of your operations.
An effective CMMS ties spare parts, consumables, and tools to locations and bins:
Stock Replenishment Rules: Minimum/maximum levels, reorder points.
Adjusting Inventory & Lot Tracking: Serial numbers, lot expiry.
From purchase orders (POs) and receipts to vendor ratings, this suite handles:
Online Purchasing: Web-based requisitions, approval workflows, and supplier portals.
3rd-Party Integrations: CAD, PDM, ERP connectors ensure parts lists and BOMs flow seamlessly.
Why It Matters: Tight integration between maintenance and procurement slashes lead times, curbs stockouts, and boosts negotiating power through vendor performance metrics.
Top CMMS platforms include a skills matrix documenting certifications, training histories, and authorized tasks per technician. This underpins:
Employee Self-Service: Technicians view their assignments, clock hours, and even request time off.
Training & Competency Tracking: Automated reminders for recertification and onboarding.
Why It Matters: Ensuring the right person with the right skills is assigned to each task is critical for safety, compliance, and quality.
Financial transparency underpins executive buy-in:
General Ledger, Accounts Payable/Receivable: Automatic journal entries per work order.
Cost Accounting & Budgeting: Track maintenance spend by department, project, asset class.
Project Accounting & Forecasting: Planned project costs vs. actuals, helping justify capital investments.
From simple “time to complete” reports to advanced Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures), OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), uptime percentages this module family turns raw data into actionable insights.
Why It Matters: With transparent metrics, maintenance becomes a strategic lever, not just a cost center.
Off-the-shelf workflows rarely match every organization’s nuance. Top systems allow:
Drag-and-drop workflow designers for approvals, escalations, or multi-step processes.
Custom fields, forms, and data models to capture unique business rules.
A modern CMMS must coexist with your broader enterprise technology ecosystem:
3rd-Party ERP Software (e.g., Oracle, SAP, Dynamics)
Wireless Handheld Devices and Barcode Technology for real-time data capture.
Shop-Floor Data Collection: Connect PLCs, SCADA, or sensor networks.
Why It Matters: Tight integrations eliminate double-entry, ensure data integrity, and create a “single source of truth.”
An intuitive UI web-based or mobile-friendly drives adoption. Features include:
Responsive dashboards, drag-and-drop scheduling boards, and customizable homepages.
Help modules with context-sensitive guidance, knowledge bases, and embedded SOPs.
For field technicians, offline capability is key:
Mobile apps that sync when online, storing data locally in remote locations.
PDA/Tablet integration with barcode scanners for quick part issuance and time logging.
Why It Matters: A CMMS that’s clunky or offline-only will sit unused; mobility is no longer optional.
More mature platforms incorporate Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) tools:
Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA) modules.
Risk matrices tying asset criticality to maintenance priorities.
Streamlined communications via:
Automated alerts (email, SMS, in-app) for overdue tasks or threshold breaches.
Approval chains, ensuring nothing proceeds without proper sign-off.
A well-architected CMMS with the modules above in harmony becomes a data lake a treasure trove of maintenance intelligence. But without governance, it risks turning into a data swamp, full of orphaned records, duplicate assets, and outdated checklists.
Best Practices:
Governance Policies: Define data owners, cleanup schedules, and naming conventions.
Change Management: Train users, document processes, and roll out modules in controlled phases.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly review module usage, retire unused fields, and refine KPIs.
When evaluating CMMS vendors, consider:
Breadth vs. Depth: Do you need end-to-end coverage, or just a few critical modules to augment an existing ERP?
Industry Fit: Some solutions are tailor-built for manufacturing, others excel in facilities or fleet contexts.
Total Cost of Ownership: Factor licensing, implementation services, infrastructure, and ongoing support.
Scalability & Roadmap: Can the platform grow with your organization adding IoT analytics, mobile fleet tracking, or AI-driven predictive insights
A concise overview of what a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is, its core purpose, and how it fits into the broader Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) landscape. This is a great starting point if you need a clear, vendor-neutral definition. CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System)
CMMS platforms are multi-faceted ecosystems of modules, each addressing specific maintenance challenges. From core work order processing and preventive maintenance scheduling to sophisticated financial accounting, mobility, and risk management, every module you choose shapes your maintenance strategy’s effectiveness. By understanding how each component works and how it’s rated against industry benchmarks you can craft a solution that not only keeps the lights on but transforms maintenance into a strategic, data-driven advantage.
Invest the time to map your operational needs against this module matrix, engage stakeholders in prioritization, and pilot critical capabilities before full deployment. With the right CMMS configuration, your organization will shift from firefighting breakdowns to engineering reliability, optimizing asset performance and driving measurable business value.

Discover how AI, cloud integration, and IoT are shaping the future of enterprise...
Read more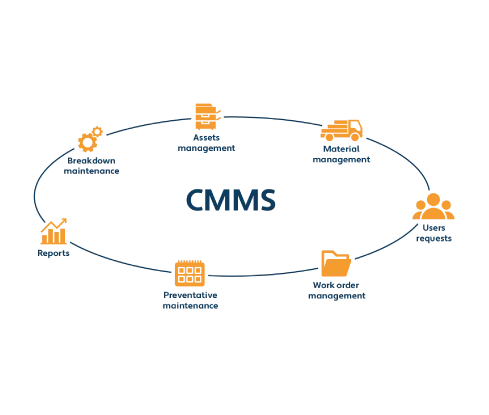
Discover key CMMS modules like work orders, PM, inventory, and reporting. Learn...
Read more
Learn how data migration can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance security,...
Read more